June 5, 2020
Air Date: June 5, 2020
FULL SHOW
SEGMENTS

#BlackBirdersWeek
View the page for this story
In the wake of a confrontation and false accusation against Black birder Christian Cooper by a white dog walker in New York City, a group of Black scientists, birders, and nature enthusiasts came together on social media to create the first ever Black Birders Week. Kassandra Ford is one of the event’s co-organizers and a PhD candidate in evolutionary biology at the University of Louisiana at Lafayette, and she spoke with Host Steve Curwood about her own experiences as a Black naturalist and how Black Birders Week is giving a voice to birders of color everywhere. (11:52)

Beyond the Headlines
/ Peter DykstraView the page for this story
This week, Environmental Health News Editor Peter Dykstra and Host Steve Curwood examine how “mad scientist” tropes in popular culture may damage our trust in the warnings of real scientists. Then, a new study linking fracking with reproductive health problems in horses. And in environmental history, they look back to the huge 1996 settlement paid by California energy company Pacific Gas & Electric for its dumping of a carcinogen. (04:48)
Border Wall Threatens Sacred Native Lands
View the page for this story
The Tohono O'odham Nation has been confined to a tiny fraction of the lands it once held in the desert Southwest. Now the Trump Administration’s border wall expansion threatens to further damage and restrict their access to sacred and archeological sites. Rafael Carranza, a journalist for the Arizona Republic and USA Today, spoke with Living on Earth’s Bobby Bascomb. (09:06)

Reopening National Parks
View the page for this story
During the coronavirus pandemic lockdown, most National Parks closed their doors to visitors, allowing wildlife including bears, pronghorn, and desert tortoises to venture into usually-crowded areas of the parks. As parks gradually reopen for the summer season, NPS employees are working to keep animals and visitors safe. Kati Schmidt, the Director of Communications for the National Parks Conservation Association, joined Host Steve Curwood to discuss the challenges of reopening National Parks amidst the coronavirus pandemic. (05:41)

Poetry of “The Park”
/ Jenni DoeringView the page for this story
Now more than ever, public parks are providing some relief for those self-isolating in cities. But some have been closed for fear of overcrowding and even without a pandemic, some public spaces may not be truly open to all. A new book of poetry called The Park uses the Luxembourg Gardens in Paris as a lens to peer into the paradox of how public green space can provide access to beauty and refuge for some, while managing to exclude others. Author John Freeman speaks with Living on Earth’s Jenni Doering and shares poems from the collection. (15:26)
Show Credits and Funders
Show Transcript
HOST: Steve Curwood
GUESTS: Rafael Carranza, Kassandra Ford, John Freeman, Kati Schmidt
REPORTERS: Peter Dykstra
[THEME]
CURWOOD: From PRX – this is Living On Earth.
[THEME]
CURWOOD: From PRX – this is Living On Earth.
[THEME]
CURWOOD: I’m Steve Curwood.
Expansion of the US border wall with Mexico continues despite concerns about sacred native American sites.
CARRANZA: There are numerous historical sites throughout the Arizona desert that are very important to the Tohono O'odham Nation, but all of these are on the path of construction and because this construction has been ongoing so rapidly, there’s a lot of concerns about how the government is treating some of these sites.
CURWOOD: Also, the unique challenges that face people of color when spending time in nature.
FORD: Our goal is to show the world that Black birders are here. Black people are enjoying nature as much as they possibly can, but there are also some issues with how Black people have to experience the outdoors.
CURWOOD: We’ll have those stories this week on Living on Earth – Stick Around!
[NEWSBREAK MUSIC: Boards Of Canada “Zoetrope” from “In A Beautiful Place Out In The Country” (Warp Records 2000)]
[THEME]
#BlackBirdersWeek
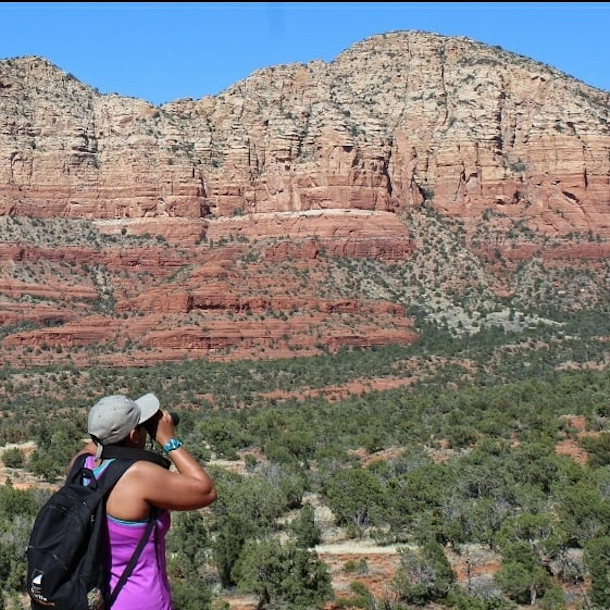

Kassandra Ford birding at Bell Rock near Sedona, Arizona. One #blackbirdersweek event asked Black scientists and nature enthusiasts to submit photos of themselves working and enjoying nature. (Photo: Courtesy of Kassandra Ford)
CURWOOD: From PRX and the Jennifer and Ted Stanley Studios at the University of Massachusetts Boston, this is Living on Earth. I’m Steve Curwood.
Back when Black lives first mattered in America, people who look like me were valuable commodities that could be bought and sold, often at high prices and often kept in place with chains. After slavery the chains of violence and discrimination still kept many of us in place, blocking us from certain neighborhoods and shortchanging us in the free labor market. And today, some white people still see Black people as “out of place” in a variety of roles, even being out in nature watching birds. In fact, for years Black birders have been warned to avoid certain times and places for birding, to avoid wearing hoodies and to always carry ID. Just recently Black birder Christian Cooper was birding in New York’s Central Park when a white woman falsely accused him of threatening her life when he complained about her unleashed dog. Now as protests continue nationwide after the horrifying murder of Black and unarmed George Floyd by policemen in Minneapolis, a social media campaign called #BlackBirdersWeek has gone viral. One of the organizers of this event and growing movement is Kassandra Ford, a PhD candidate in Evolutionary biology at the University of Louisiana at Lafayette, and she joins us now. Welcome to Living On Earth!
FORD: Thank you for having me, Steve.
CURWOOD: So how did the movement to start Black Birders Week get started?
FORD: So Jason Ward, who is a pretty prominent Black birder on Twitter, actually created an online group of Black people, who are all in STEM or research fields, to kind of get together and talk on a semi-daily basis. We talk about life. We talk about science, we talk about birds, and even some social issues as well. When the incident happened in Central Park with Christian Cooper, we saw it as an opportunity to spark a movement and a discussion. So by highlighting some positive things that are happening in the birding community, highlighting some amazing Black birders and trying to inspire some new Black birders, we hoped to make something positive out of the situation that arose in a pretty negative light. Our goal is to show the world--pretty much at this point we have a global reach--that Black birders are here, Black people are enjoying nature as much as they possibly can. But there are also some issues with how Black people have to experience the outdoors and issues with making sure that Black people and people of color can remain safe while doing so.
CURWOOD: What's the experience of birding while Black?
FORD: Well, a lot of people have had a lot of different experiences. One of the most prominent experiences that people are probably familiar with is the incident that happened in Central Park with Christian Cooper. Being an African American person and trying to do birding or anything in the natural world can be somewhat dangerous. We can't just experience the outdoors as a white person would. Instead we do sometimes have to take precautions and sometimes we have incidents with the public or with police officers that are not always positive. A lot of people in the group that I am a part of here that's organized and started Black Birders Week, we all have experiences.
CURWOOD: Talk to me about a situation where you felt constrained to be outdoors birding, fishing, whatever, as a person of color.

Kassandra Ford is a PhD student studying the evolution and morphology of electric fish at the University of Louisiana at Lafayette. She also helped co-organize the #BlackBirdersWeek movement. Here she is birding at Denali National Park in Alaska. (Photo: Courtesy of Kassandra Ford)
FORD: As a person of color, I have definitely felt some constraints. There are certain times of day that I will not go outdoors and go on I guess like field expeditions you might call it to go look for animals. I won't go in the middle of the night. Very first thing in the morning is also a time of day that I won't go alone. If I was with a group of people, I might be a little more keen to go, but if it's just me, I stick to middle of the day when I can be easily seen and my intentions understood. A lot of us as Black naturalists also carry equipment prominently showing to kind of show what we're doing and why we're doing it. We might carry our binoculars and cameras and field guides and wear hats that have logos for naturalist organizations showing so that it's pretty clear to bystanders or people around us that we belong there.
CURWOOD: Now, to what extent are Black birders an endangered species?
FORD: I like to think they are a recovering endangered species in the sense that our numbers are growing constantly. I think especially given this movement slash hashtag that's coming out of Twitter. We're seeing thousands of people submitting pictures of them going outdoors, finding birds, having a blast, and you don't have to be a professional to consider yourself a birder. You don't need to own binoculars. You don't need to own a fancy camera. All you need to do is go outside and look up, look into the trees and see if you can find one.
CURWOOD: Hey, Kassandra, what's your favorite bird?
FORD: My favorite bird. I would have to say the Scarlet tanager. It's actually a bird that I saw for the first time this year. We were actually really blessed here to be home for quarantine I guess during spring migration. And our backyard was magically a hub for all of these different migrating birds that I had never been able to see before. And so I saw a scarlet tanager and it was breathtakingly gorgeous. It was unlike anything I'd ever seen before. But it is bright red, but it has dark Black wings. And so it contrasts to its body and male Scarlet tanager is so pretty.
CURWOOD: So by the way, who were your role models in science? I mean, what did you see in the way of representation of Black scientists and ecologists while you were growing up? And what sort of advice do you have for people coming up behind you now?
FORD: Unfortunately, I really didn't have a whole lot of role models that looked like me. Growing up, and even in college, I went to the University of Wisconsin, Madison, and the biology department there is predominantly white, and also predominantly male. And I kind of had to forge my own way, as a Black woman. But I was lucky enough to have some awesome women mentors to kind of show me the way and really inspire me into getting into research. And I was always good at biology, biology was, that was my subject, but it really took going to college and taking some of those higher level classes that really got me thinking about the roots of science and asking questions and trying to figure out how you can answer them. And then once you get those answers, it just leads to more and more questions. And that's probably the thing that I love the most about science is the never ending questions, which some people probably find frustrating, but I fell in love with it. And so advice to kind of that up-and-coming generation, the next people who are going to be our amazing scientists in the future would be: go outside and just start asking questions. You don't have to find out the answers yet. But just starting that process of critical thinking is a really, really important, and I think fun exercise and anyone can do it.
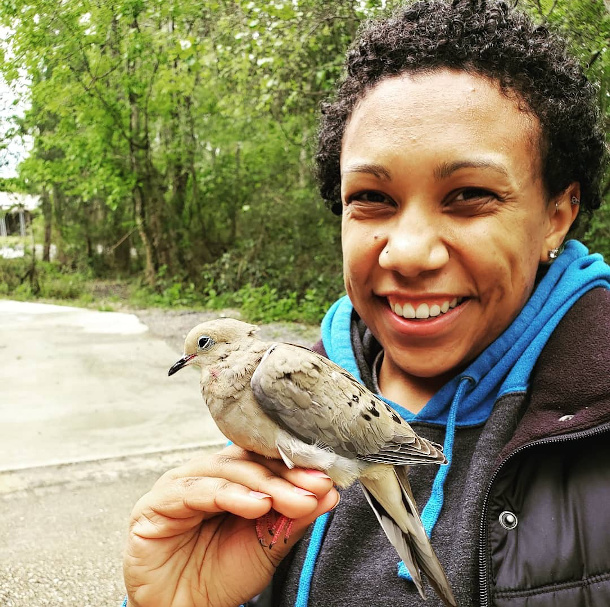

Kassandra Ford holding a Mourning Dove at an Audubon banding station in Bluebonnet Swamp, Baton Rouge, Louisiana. This bird was handled under a banding permit. (Photo Courtesy of Kassandra Ford)
CURWOOD: So the natural world for many people represents a refuge from a lot of the turmoil of our daily realities, whether it's politics or economics or social or traffic, whatever. To what extent do you feel that same refuge when you go out into the natural world?
FORD: I feel it quite a bit. But unfortunately, I am not sure I will ever experience quite as much of a refuge as a person who is not a person of color. So I personally love the outdoors. It's my happy place. It's where I go to have fun and see new things that I've never seen before. But as a Black person, it's also a place where I have to regularly check my surroundings and always kind of have an eye open in the back of your head and make sure that what you're doing is that you're doing something as safely as you possibly can.
CURWOOD: To what extent have members of the outdoor community, the scientific community, been welcoming to you in and in your opinion, what sorts of things could those groups do to make nature a more accessible resource for people of African descent in the United States of America.
FORD: I would say that predominantly societies and the people within them to me have been incredibly welcoming. I have actually had some people that before this, I had just considered Twitter acquaintances, somebody that I might have met for five minutes at a society meeting, or conference, who have really shown up for us. They've been pretty big allies in this conversation and this movement that we're doing in terms of they not only listen and truly care about what people of color and Black people are saying, but they're willing to set aside their own personal voices to amplify our own.
CURWOOD: So what sort of change in the world do you hope this movement can create?
FORD: I hope it creates interest in both Black people and non people of color to go outside and enjoy nature more and appreciate it and work with their local natural organizations and go out and do something that they've never done before, whether it's a local hike at a park, whether it's going to an Audubon event and doing some bird banding and seeing a bird up close that they've never been able to see before. But I really hope that people, regardless of race, take this as an opportunity to really go into nature and appreciate it as much as they can. But at the same time, I also hope that people who are not people of color take this as a positive thing that has come out of a lot of historically negative situations. So whether it was a Central Park incident or any of the incidents that have involved police brutality, we hope that we can spark a conversation to address the problems that are about race in this country and really see if there's a way for us to move forward and make things better and safer for everyone involved, but especially safer for Black people.
CURWOOD: Kassandra Ford is a co-organizer of Black Birders Week and a PhD candidate in evolutionary biology at the University of Louisiana at Lafayette. Kassandra, thanks so much for taking the time with us today.
FORD: Thank you for having me. It was truly fun.
Related links:
- CNN | ‘These Black Nature Lovers Are Busting Stereotypes, One Cool Bird at a Time’
- Follow @BlackAFinSTEM on Twitter for more updates and events
- The BlackAFinSTEM website
[MUSIC: Holly Near (Jorge Ball Vargas and Horacio Salinas Alvarez) “La Marusa” on And Still We Sing, by Jorge Ball, Calico Tracks Music]
CURWOOD: Coming up – the national parks and the pandemic is just ahead here on Living on Earth
ANNOUNCER: Support for Living on Earth comes from Sailors for the Sea and Oceana. Helping boaters race clean, sail green and protect the seas they love. More information at sailors for the sea dot org.
[CUTAWAY MUSIC: Holly Near (Jorge Ball Vargas and Horacio Salinas Alvarez) “La Marusa” on And Still We Sing, by Jorge Ball, Calico Tracks Music]
Beyond the Headlines

Science denial may have ties to pop culture portrayals of scientists as ‘wacky’ or ‘nerdy’, downplaying their competence. (Photo: U.S. Army Combat Capabilities Development Command, Flickr, CC BY-SA 2.0)
CURWOOD: It’s Living on Earth, I’m Steve Curwood.
It's time now for us to take a look beyond the headlines with Peter Dykstra. Peter’s an editor with Environmental Health News, that's EHN.org, and dailyclimate.org. He is joining us now on the line from Atlanta, Georgia. Hey there, Peter, what's going on? What do you have for us today?
DYKSTRA: Hi Steve. You know, I've been thinking a lot this week, seeing these scenes in the lake of the Ozarks, the East coast, the West coast and beaches, nighttime and parties, of people pretty much ignoring the stern advice from scientists about maintaining social distance. That reminds me about a long-term problem our society has with scientists.
CURWOOD: And that would be?
DYKSTRA: Well, go back to the 1818 when Mary Shelley published her epic novel "Frankenstein," about Dr. Victor Frankenstein, the classic evil scientist from culture, creating a bad thing, the Frankenstein monster. You take that all the way to the 1990s and you have Dr. Evil, the comic version of an evil scientist, and many, many more sort of cementing the evil scientist brand of why we shouldn't like or trust what we hear from scientists, whether it's climate change or the coronavirus.
CURWOOD: Well, and not just evil scientists, though. I mean,
DYKSTRA: Yeah, I've listed several of them. I wrote about this for EHN this past week. You've not just got the evil scientists but the more benign types. Let's just take a minute, Steve, you have to have a favorite goofy scientist or evil scientist from years of TV or movies. Who's your favorite?
CURWOOD: Well, I guess as a kid, I liked Mr. Wizard, but of course, in the movies, Eddie Murphy, the nutty professor, he's the guy!
DYKSTRA: Oh, Eddie Murphy was great. That was a remake of a 1963 movie, The Nutty Professor, played by Jerry Lewis. That's a lasting impression that we have. You've not just got the evil scientist but the more benign type, the goofballs like Doc Brown from the Back to the Future movies, socially inept scientists like the cast of The Big Bang Theory--just completed the 12 year super successful series run on TV--all the time cementing the ideas that scientists are the ones we trust least. They're the ones that got roughed up in gym class or picked last for basketball, or who sat out the senior prom. And all of those things create a lasting image of scientists in pop culture that are probably a huge factor in why we have trouble listening to scientists when they tell us what's needed to beat the coronavirus or they tell us what's needed to beat climate change.
CURWOOD: Yeah, it's a tough one too. And science knows best about climate change. science knows best about pandemics. Hey, what else do you have for us this week, Peter?
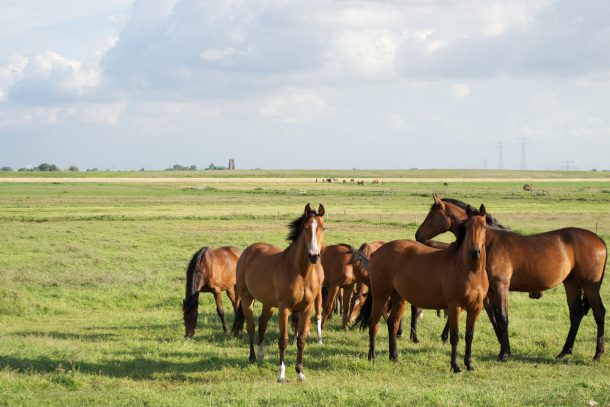

Fracking has been linked to a birth defect in young horses, whereby nursing foals inhale milk rather than swallowing it. (Photo: Feltkamp, Flickr, CC BY 2.0)
DYKSTRA: One of my colleagues at EHN, Kristina Marusic, has written for several years on potential health problems in areas where fracking is dominant. A few years ago, she wrote about links between fracking and depression. Just recently she published a story based on a peer-reviewed bit of science. They studied horses owned by the same man in two areas, one where there was fracking, one where there wasn't, and the horses in the fracking zone had some serious problems with reproduction: high risk pregnancies that led to a big disparity in healthy births among the horses.
CURWOOD: Hey, let's take a look at history now Peter. Right now this is June of 2020. What do you see going back?
DYKSTRA: Let's go back to June of 1996. Specifically June 12th, when Pacific Gas and Electric, PG&E, one of the biggest utilities in the country, agreed to pay a third of a billion dollars--$333 million--to residents of the small town of Hinkley for contaminating their drinking water supply with chromium 6, one of the biggest, baddest pollutants across the country. But PG&E has continued to have a bad track record after that one third of a billion dollar-payout. And then in 2018, the most famous, the worst, the most tragic of all where malfunctions in PG&E power lines set a blaze that burnt the town of Paradise, California to the ground. PG&E has already committed to paying $13 billion to the residents and former residents and survivors of residents in Paradise. And with such a big amount on the liability side, Pacific Gas and Electric has declared bankruptcy.
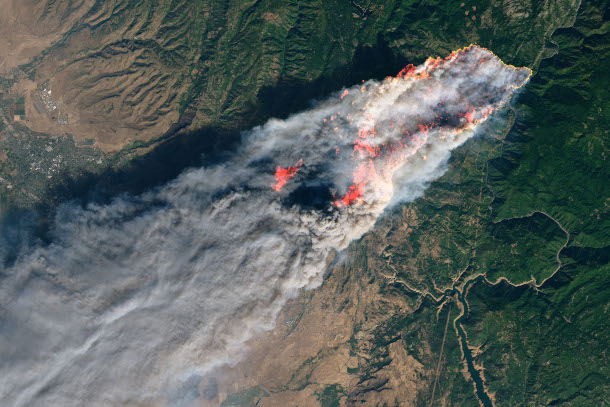

Pacific Gas & Electric has been criticized by U.S. District Judge William Alsup, saying the company poses a threat to the safety of the people of North California. Joshua Stevens, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Flickr Creative Commons)
CURWOOD: Peter Dykstra is an editor with Environmental Health News. That's EHN.org and dailyclimate.org. We'll talk to you again real soon.
DYKSTRA: All right, Steve, thanks a lot. Talk to you soon.
CURWOOD: And there's more on these stories at the Living on Earth website. That's LOE.org.
Related links:
- Environmental Health News | “They Blinded Us with SCIENCE!”
- Environmental Health News | “Fracking Linked to Rare Birth Defect in Horses: Study”
- KQED News | “Judge Rips PG&E for Poor Safety Record Leading to Wildfires”
[MUSIC: Thomas Mapfumo/Wadada Leo Smith, “Marimuka/Collecting My Father’s Wealth” on Dreams and Secrets, by Thomas Mapfumo, Anonymous Web Productions]
Border Wall Threatens Sacred Native Lands
Quitobaquito Springs is home to two desert-native endangered species, and groundwater drilling for the border wall could deplete the aquifer that feeds the spring that many rely on for water. (Photo: Kevin Dahl, NPCA, CC BY 2.0)
CURWOOD: The pandemic and economic slowdown have not stopped the construction of more sections of a wall along the US border with Mexico. The border wall was a key promise of President Trump’s election campaign, and in his bid to keep that promise, dozens of environmental laws from the Endangered Species Act to the Clean Air Act were suspended to fast track construction. Some Native Americans say that, without such laws in place, their sacred ancestral lands, including burial grounds, have been desecrated. The Tohono O’Odham nation along the border in Arizona is objecting to the bulldozing of these lands. Rafael Carranza writes for the Arizona Republic and USA Today and visited several Native American sites where wall construction is moving forward. He spoke with Living on Earth’s Bobby Bascomb.
BASCOMB: I understand that you visited several tribal areas that will be impacted by the border wall, but they're considered sacred by the tribal people who live there, the Tohono O'odham. Can you tell me about that trip, please?
CARRANZA: Yeah, so all of this happened before the coronavirus pandemic. And there are numerous archaeological historical cultural sites throughout the Arizona desert that are very important to the Tohono O'odham Nation here. These are protected lands. It's you know, desert wilderness. But these contain signs of the early tribal life that the O'odham people carried out for centuries and centuries. So in January, we had the chance to visit these sites that are located at the Organ Pipe Cactus National Monument, as well as Cabeza Prieta National Wildlife Refuge including Monument Hill, Quito Baquito Springs which is a natural source of water for dozens of miles around. There's also a ceremonial site called Las Playas and an unnamed burial site that's located immediately next to the border wall. So all of these are on the path of construction. And there's a lot of very valid concerns that the tribe has brought up about, you know, how the government is going about in treating some of these sites. And, you know, frankly, like their involvement as well. They want to be involved in the whole process, because they understand that you know, these are their ancestors, this is their culture and their heritage.
BASCOMB: Can you please give me a little bit of history about the Tohono O'odham in this region and the cultural importance of the land for them?
Saguaros torn down to make room for the border wall construction. (Photo: Kevin Dahl, NPCA, CC BY 2.0)
CARRANZA: Yeah, so the Tohono O'odham people, they have lived in these areas for centuries and centuries. They've inhabited these lands before there was the United States and before there was a Mexico. So a big part of their culture involved the traveling of the desert. They would set up and live in areas following the water, following a lot of the resources of the land. It's a very parched area so it was a constant struggle, you know, looking for food and water and so they would travel vast territories stretching from the Colorado River on the Arizona-California state line, all the way to the San Pedro river in the eastern part of Arizona, and they would stretch as far north as Phoenix as far south as the state of Sonora. So it's a very, very large territory that compromises the Sonoran Desert. They've lived here for many, many centuries and over time, you know, the US government created the reservation for them close to the US-Mexico border. And so because they traveled so extensively throughout the region, once the borders were instituted, what ended up happening was that a large portion of the tribal members ended up being in the United States, but then a large portion of them remained in Mexico. And unlike the United States, the population of Mexico doesn't have a reservation or protected lands that are, you know, designated exclusively for the tribe. So that has created a lot of issues with the community because access to a lot of those historical sites and a lot of the pilgrimage routes and a lot of the areas that are important to their culture are increasingly harder to get to on the Mexican side. And increasingly now in the United States as well, it's because of all the border security mechanisms in place.
Ancient saguaros being removed for border wall construction. (Photo: Kevin Dahl, NPCA, CC BY 2.0)
BASCOMB: So the nation of people was separated by an international border, which of course, was difficult and now from what I understand they want to improve the border wall that runs through the area, how will that affect them?
CARRANZA: The US government has really pursued and the Trump administration in particular has been aggressive in erecting a new design, a new type of barrier, along the entire length of the US Mexico border, at least in areas where it's easier for them to get to at the moment. These are sites that are not within the reservation, but they are protected federal lands. So the US government already has control of them. So it's relatively easy for them to issue the waivers on some of these laws and then expedite and move construction, you know, full speed ahead. And they have in fact been doing that for the past few years now. Because this construction has been ongoing so rapidly. The tribes have complained that they are just not being taken into account, that their voices are not being heard and their concerns are not being addressed when it comes to the erection of these new taller barriers in a lot of these sites. That you know previously already had something, they may have had a vehicle barrier, so they have shorter steel slats, but the Trump administration has been pushing 30 foot tall bollards, you know which tower above anything else that you would see in these parts of the border and in the desert. And I'll have to point out that you know, the Tohono O'odham Nation, because they do enjoy a lot of tribal sovereignty and you know, they wield a lot of influence and control over the reservation itself, they've been able to keep the United States from building any sort of barriers like 30 foot tall bollards within their reservation. A lot of the construction has really focused on the areas outside of that reservation like areas that the government already controls. And so there are currently no plans to do any border wall construction on the Tohono O'odham Nation itself because the nation has not allowed it. And it's very likely, you know they'll continue resisting as long as they can. What they do have is some of the towers and cameras and sensors and some of the other technology that they're advocating, you know, could be better served, but they don't have any border wall construction itself on their lands.
BASCOMB: And from what I understand the new border wall that's being constructed or the improvements to it, they are actually unearthing human remains. It's an ancestral burial ground for the Tohono O'odham. How's the tribe responded to that?
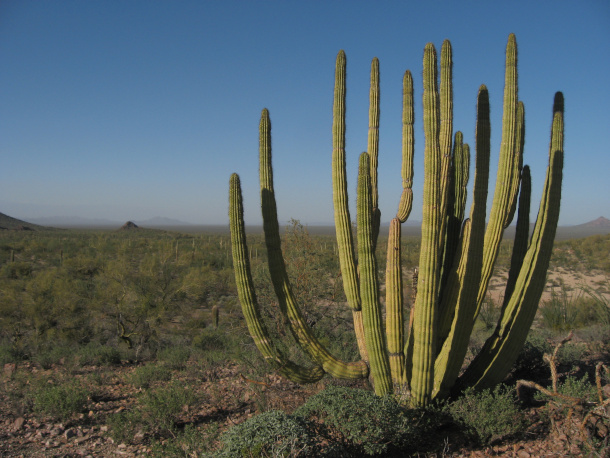

The Organ Pipe Cactus National Park in Arizona is the only area where Organ Pipe Cactus grows wild. The Tohono O’odham Nation is one of the many tribes which considers this land sacred. The construction of the border wall involves heavy machinery that has already damaged wildlife and cacti in the Arizona desert. (Photo: Ken Lund, Flickr, CC BY SA 2.0)
CARRANZA: Yes. So in October, the contractors that were preparing to build the border wall, that organ pipe, as they were, you know, doing those preparations, they came across some possible bone fragments. And so they did some testing, they determined that it was actually human remains. So whenever these remains were found back in October, the work was stopped and the government was able to recover the fragments and they're in the custody of the National Park Service, who will then hand them over to the Tohono O'odham Nation. But the nation and the tribe, they've really been very concerned that that's just one reported instance but that there could be many more instances where the contractors or the construction workers don't know what to look for and so there's concerns that their heritage will be irreparably damaged. And I'll mention that, you know, the US government does have environmental monitors and cultural monitors that they hired to have on site in case that they do come across any endangered species or cultural artifacts and so on, but they only have one person that, you know, monitors the entire swath of construction in this entire desert region where where the project is ongoing now. So, the tribe has been very concerned that things will fall through the cracks and that ultimately these sites will be damaged and that you know, a lot of the artifacts that are found there will be lost or damaged forever.
BASCOMB: So how likely is it at this point that the wall is going to go on as the government plans or might there still be something that puts a stop to it, considering this cultural significance of the area that they're planning to build on?
CARRANZA: You know, there seems to be very little indication that the government will change their plans or alter their plans in any significant way or fashion. They are moving ahead and proceeding as they had delineated from the beginning. The goal is to have all of these barriers here and Arizona finished pretty close to the election in November. So they're, you know, moving full speed ahead and the concern that environmentalists and the tribe are bringing up is that because, you know, they seem to be moving with this particular deadline in mind, that they're just not taking them into account or consulting with them, because that would require more time and could delay a lot of their efforts. And so environmentalists and community groups are hoping that the courts will be able to step in through one of the several lawsuits that they filed. They're hoping that the federal judges will either issue an injunction barring the government from any additional construction or any other type of measures that will stop the construction at the moment. But to date we haven't seen any of that.
CURWOOD: That’s journalist Rafael Carranza speaking with Living on Earth’s Bobby Bascomb.
Related links:
- Arizona Central | “Tohono O’odham Historic Sites at Risk As Border Wall Construction Advances in Arizona”
- Arizona Central | “Video Shows Groundwater Drilling Near Sensitive Spring as Border Wall Construction Continues”
- LA Times | “Arizona Tribe Refuses Trump’s Wall but Agrees to Let Border Patrol Build Virtual Barrier”
[MUSIC: Los Lobos, “Kiko and the Lavender Moon” on Kiko, by D. Hidalgo and L. Perez, Slash/Warner Bros]
Reopening National Parks
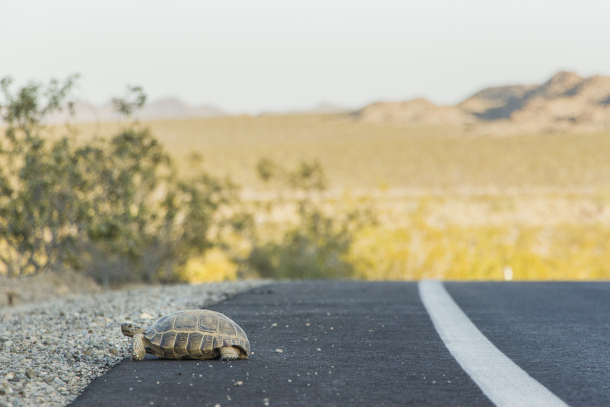

During the months Joshua Tree National Park was closed, there was less vehicle traffic, which allowed desert tortoises a safer road crossing. (Photo: Brad Sutton, NPS, Flickr, Public Domain)
CURWOOD: There are more than 400 parks and other public spaces administered by the US National Park system, and most were closed as the pandemic surged. Warmer weather and the urge to get outside in nature as an antidote to the confinement of quarantine is pushing the park system to open up more now, though it seems the animals in many parks did not miss us. Rangers in national parks including Yosemite, Rocky Mountain and Death Valley report seeing wildlife temporarily reclaim some spaces typically full of visitors. But now the National Park Service has to find ways to re-open which will keep the animals, visitors and staff safe as the pandemic continues. Kati Schmidt is Director of Communications at the National Parks Conservation Association.
SCHMIDT: With the national parks being closed in places across the country for varying amounts of time up to, you know, two months, some even longer, it really gave an opportunity for the long term, you know, full time inhabitants of our national parks, the wildlife, to really come out. And for example, in Death Valley National Park, a herd of pronghorn antelope, they were found as low as the Furnace Creek area of the park, which is normally a very busy area of Death Valley and somewhere where a lot of colleagues had shared that this was unprecedented--that they had never seen pronghorn in that area of Death Valley before.
CURWOOD: So Great Smoky National Park is, I believe, the most visited National Park and therefore I guess the critters there would all of a sudden say wait, nobody's here. Which of those critters came out to be seen by you know those few rangers that were still there?
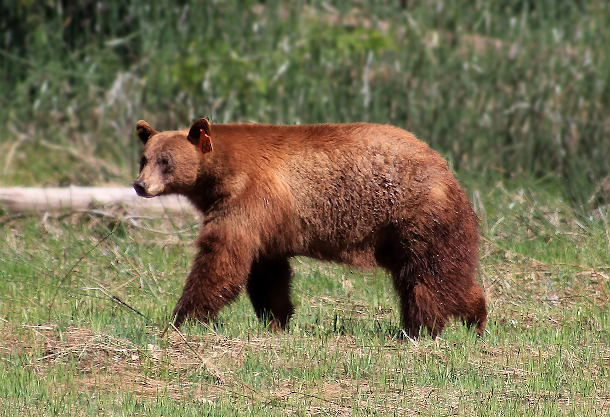

Picture of a black bear in Yosemite National Park. (Photo: Dave Toussaint, Flickr, CC BY NC 2.0)
SCHMIDT: You know, there were reports of black bear moms and cubs coming out of hibernation and being seen in what are normally high traffic public areas of the park. From a wildlife perspective, if you think about animals like bears that do have a longer lifespan that could be the first time in years that they are coming out in the spring season to not have hordes of cars driving by with their cameras out.
CURWOOD: Now what's been seen in the West there, what about Yellowstone? What critters are venturing out that are not seen nearly as often as have been seen in these past couple of months.
SCHMIDT: In Grand Teton in Yellowstone, the famous grizzly bear 399 and her new set of cubs were recently seen coming out of hibernation in the park. Down in Joshua Tree National Park park rangers were reporting especially during the park closures, a lot of desert tortoise coming out of their boroughs and finding some sunshine on roadways. Now, during the park closures finding sunshine on roadways seemed like a pretty good idea if you're a desert tortoise looking for a hot place to hang out, but obviously during normal times, that would be kind of a kiss of death for a desert tortoise. So Joshua Tree has done a really great job at educating visitors as they enter the park. They have little tortoise shaped flashing signals of you know slow down look out for tortoise. Desert tortoise is one of more than 600 protected species under the Endangered Species Act that have habitat in our national parks. So it's really important to think about protections for those animals and also the bigger role that protecting an animal in its habitat has on protecting the bigger park ecosystem.
CURWOOD: As the parks open, to what extent are they getting overwhelmed by people just eager to get out of quarantine?
SCHMIDT: You know, Memorial Day weekend was really a wake up call. We saw up at Grand Canyon a line of cars outside of the entrance to get in. The park only had their entrance gates open for four hours in the morning and really limited opportunities. As parks reopen we're concerned that in some cases they are reopening too soon and we're concerned in many cases that we're not sure whether the parks have the proper equipment PPE within the National Park to help serve their stuff and to ensure visitor safety. A number that continues to stick with me is that in the entire Morongo Basin surrounding Joshua Tree National Park, there are only four ICU beds. So many national park communities are really kind of more isolated from urban centers, so there is a lot of concern for both park staff as well as surrounding communities if parks do reopen too soon.

In Death Valley National Park, pronghorns have been spotted near park headquarters, where they are typically not seen. (Photo:Jim Choate, Flickr, CC BY-NC-ND 2.0)
CURWOOD: I noticed that in the past year, Yosemite Valley had to limit the amount of visitors due to high levels actually of littering and even human waste that were along the entrance roads, especially the south entrance. So this begs the question: Should the national parks limit the amount of visitors allowed to enter the parks in order to avoid issues such as excessive trash, overwhelming the rangers and for that matter, overwhelming animals who act as if maybe they could use more of the territory that they’re allotted?
SCHMIDT: The idea of you know, parks being loved to death has been kind of a narrative of the last several years. But as some parks have started to reopen, we've seen some proposals of parks putting in different timed entry protocols in place. Rocky Mountain is the first National Park that did get approved to do some timed entry as they reopen the park. You would buy a ticket for a specific time and day. And that allows the parks to monitor both days that are busier and also be able to space things out a bit and to hopefully ensure that when people go to parks like Yosemite, they're actually able to not just spend the whole time sitting in stopped traffic, but actually get out of their cars and enjoy the wonderful features.
CURWOOD: Kati Schmidt is Director of Communications at the National Parks Conservation Association. Kati, thanks so much for taking the time with us today.
SCHMIDT: Thanks so much for having me, Steve.
Related links:
- The Guardian | “‘We’ve Never Seen This’: Wildlife Thrives in Closed US National Parks”
- Learn more about the bipartisan bill: The Great American Outdoors Act
- Click here for more information of when National Parks are reopening
[MUSIC: Will Duncan and Bobby Horton, “Peace At Last” on The National Parks – America’s Best Idea (The Soundtrack), by Will Duncan, The National Parks Film Project/PBS Distribution]
CURWOOD: Coming up – City parks can be a refuge, but they’re not always equally open for all. That’s just ahead on Living on Earth.
ANNOUNCER: Funding for Living on Earth comes from you, our listeners, and United Technologies, combining passion for science with engineering to create solutions designed for sustainability in aerospace, building industries, and food refrigeration.
[CUTAWAY MUSIC: Dele Sosimi, “Ghedu 1” on Afrobeat…No Go Die!, by Dele Sosimi, Shanachi]
Poetry of “The Park”
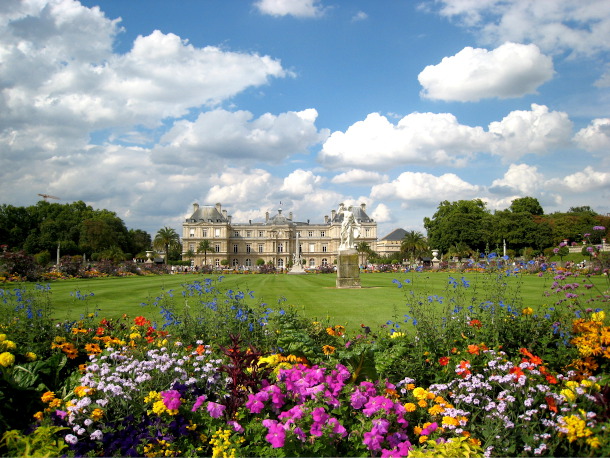

The Luxembourg Palace surrounded by the Jardin du Luxembourg in Paris, France. (Photo: Rdevany, Wikimedia Commons CC BY-SA 3.0)
CURWOOD: It’s Living on Earth, I’m Steve Curwood.
Now more than ever, public parks are providing some relief for those self-isolating in cities, as it’s harder to spread the virus outdoors in the sun and easier to keep distant from other people. Yet some parks have been closed for fear of overcrowding and even without a pandemic, some public spaces may not be truly open to all. Author, editor and literary critic John Freeman has published a new volume of his poetry called The Park, that explores how public green space can provide access to beauty and refuge for some, while managing to exclude others. John Freeman spoke with Living on Earth’s Jenni Doering.
DOERING: John, before we launch into the poems and themes of this collection, could you please tell us a little bit about how you came to write this book?

“The Park” is John Freeman’s second book of poetry. (Image: Copper Canyon Press)
FREEMAN: For the last five, six years I've been living in the summers and winters in Paris. I know you can play your little violin for me right now how sad that sounds. But most of the time, I stay on a block near the Luxembourg Gardens. And so I've gotten to know the park there very, very well in different seasons. And it's become a kind of second home to me. And I've studied it and lived in it and grieved in it, and missed people in it and met friends in it. And so to me, it feels like another part of my mental circulatory system. And in the last couple years as our nation in the US has gone through this spasm of anxiety over what a citizen means I've been spending part of that time in a park, which to me is a kind of giant metaphor for how we live together and who we allow in and who we kick out. So I began to write poems in the park, not really thinking in those terms right away, just simply observing the park. And gradually, as I transferred them from my notebook to my computer, I realized I was, I was thinking about more than just a park, but about how we live together.
DOERING: Yes, I mean, parks are these spaces that we manufacture, that we sort of like try to echo nature within them. But I think one of the things in your book is this like separation that happens in that process, right. And I wanted to ask you to read a poem, the very first poem in your collection called 'The Sacrifice'. And I think it really kind of like speaks to this idea of, of separation. Could you read that poem for us, please?
FREEMAN: Of course.
'The Sacrifice'
The difference
between animals and us
the main one is
they don't need to know
it's a park. The coyote
lopes through
just the same
looking for food. We
stop, in mourning,
sensing everything
we've lost. We call
that ceremony
a park.
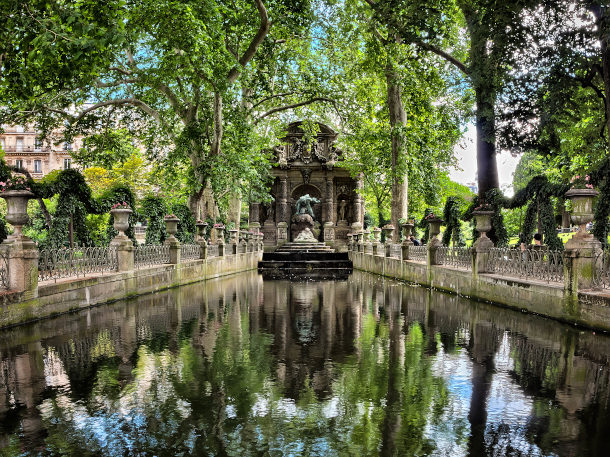

The Medici Fountain is a must-see highlight of the Jardin du Luxembourg. (Photo: Joe deSousa, Flickr CC 1.0)
DOERING: Yeah, I was really struck by the word mourning and you know, this reflection you have on everything we've lost when you're talking about how humans interact with a park. Can you say a little bit more about what you're trying to explore in this poem?
FREEMAN: Well, there's a, there's a kind of broken relationship between ourselves and nature because of our total dominion over it, and how we've begun to see it as entirely fungible, as something to be used and deployed. And even when we're trying to reattach ourselves in some emotional and metaphysical way to nature, we're still having total dominion over it as we are in a park where we decide which trees to plant there, which animals to trap and which to let run wild, when to allow people in and out as we're part of nature too. And so even though it can be made in the best intentions and still provide a great deal of comfort, a park is still a living reminder of our detachment from nature. And so as I was writing this book, I wanted to try to think about the ways that that's a feeling that goes from us towards nature and not the other way. And the sense that as you're in a park as you're in any space, the natural world is all around you. It's pushing up through sidewalks, it's taking over benches, it's leaning down upon you from trees, birds are there, and other forms of wildlife and insect life. And to all those forms of life, it's just the world. We're the ones who see the boundary between ourselves and nature and, and even a park inscribes that boundary again, as it's trying to kind of leap over it.
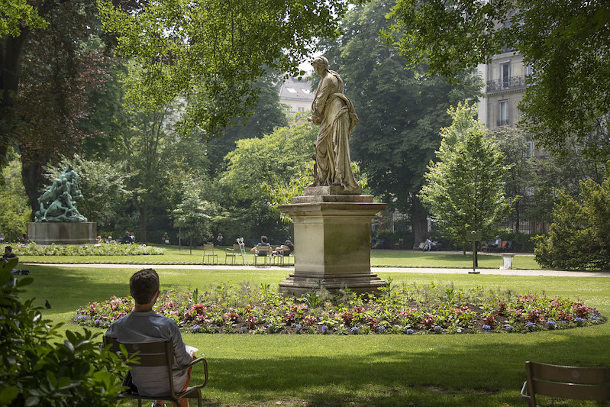
The Luxembourg Gardens contain over a hundred statues, monuments, and fountains. (Photo: Erin Johnson, Flickr CC BY-NC 2.0)
DOERING: One of the themes in in your book, The Park explores the paradoxes of public parks being open to all, yet they also manage to exclude some people as you were talking about. Could you elaborate on like, that as an observation that you made while in the Luxembourg Gardens, and the types of people that you saw as being excluded?
FREEMAN: Yeah, Paris has a fascinating history about itself and the parks. right near Luxembourg Gardens is the Place Saint Sulpice, and there's a statue in the center of that Plaza with a fountain of the four directions and it was built by a prefect who decided that all of Paris should be filled of parks and also with water fountains. This prefect ended up building over 1000 fountains across Paris. But in the century since then, there's just been several centuries of exclusion, who can stay in a park, what hours they're allowed to be there. And when I was living in Paris, especially in the last couple years since the Syrian civil war, you would see migrants who, some of whom who had even walked all the way to Paris from a war zone, were living in the park, and once Macron was elected, he was quite brutal about excluding migrants from public spaces, pushing them out of the city pushing them out of parks. And so one of the first things I saw when I would go to the park in the morning was who was moving in a way that they didn't want to be seen. And I was watching them slip through the shadows and eventually leave the park. And then one of the strangest kind of ironies of that moment was the park itself, the outside fences, often hold a kind of exhibit. At one point there was an exhibit of Syrian refugees, while simultaneously there were actual Syrian refugees in the park. I found that hypocrisy really hard to take sometimes, because the park encourages you to have a meditative mode and kind of expansive mode of thinking and people once they're in the park tend to be pretty tolerant of each other of being around each other. And yet there are all these official policies which say certain people are not allowed. So one of the things I should say is that there are other parks in this book. And I've written about things I've seen in other parks, because to me, the entire globe is one park, if you consider the world as a kind of built environment and the parks and the park systems that kind of knit their way across various nations are, to me, in some ways a kind of Uber Park. There's a kind of shared ecosystem that a park has and is a series of shared assumptions.

A bronze sculpture of a stag, doe and fawn in the Luxembourg Gardens. (Photo: Ed Webster, Flickr CC BY 2.0)
DOERING: Yeah, I mean, when you're in one particular Park, does it sort of bring up all these feelings that you've had before from other places that you've been? And is it a place where we are able to sort of get in touch with the memories that we've made in other spaces too?
FREEMAN: I think so. I mean, as a joke, I sometimes go to this place called Freeman Plaza. There's a little bench there, and the strip of grass is about the size of the desk I'm sitting at. It's right before the entrance to the Holland Tunnel. But occasionally I'll see birds there and other animals. And no one's ever sitting there because it's so loud. And I, as a test to myself, I once sat there and I thought, does this, does this really feel like a park? And to me, one of the things that I think all parks share, and which I'm trying to write about here is that the space of the park does eventually connect to the space of your mind. And so if, if you're in a space like a park, no matter how small and grubby, if it can open up the park in your mind, then you've entered into that, that kind of Uber system of parks, the one connecting each little contained space to the next but also, hopefully one connecting your mind and your, your internal space to the minds and internal spaces of others. And that's why I think parks are so genuinely humane, even if they have some restrictions about who's let in.
DOERING: Yeah, actually one of the things that I was thinking about a lot as I was reading this book, and these poems was this contrast between, you know, there's a lot of sadness and violence that you're talking about, but also these moments of kindness and tenderness between human beings and--maybe human beings and the natural world. Would you like to reflect a little bit about parks as these spaces that can open that possibility up, of tenderness between each other?

The statue “Joies de la famille”, or Joys of family, by Horace Daillion (1885), in the Luxembourg Gardens. (Photo: Jeanne Menjoulet, Flickr CC BY-ND 2.0)
FREEMAN: I'm so glad that you brought that up. I think, as a world, as a society, as a group of humans, I think we're desperate for tenderness. Because we've been seeing broadcast and on social media and on all the ways that we get information, it’s opposite for so long. And right now in the middle of this pandemic, I think people are rediscovering the power of tenderness because we're with each other more. And to me, parks were always in a way, kind of a shortcut to that feeling that capacity for tenderness. Because when you go into a park like the Luxembourg Garden, I gotta believe that your heart rate slows, your blood pressure probably lowers, your way of thinking changes and your capacity to be around others expands. And there's no better contrast and the difference between say being on Twitter, where you get none of the signals between face to face communication and tone of voice and body language smells, touch. And so people are meaner to each other. They just are. And cognitive scientists have studied the way we do that when we do mostly face to face communication versus computer-mediated communication. And the park is to me the ultimate retreat back into the full capacity of human-to-human communication. And in that sense, I think we need these spaces desperately. We need them in cities. We need them in towns, we need them in the countryside. We need places where people can get out of the spaces that bring out the worst in us to those that bring out a more thoughtful register. And I was trying to create a literary park in that sense that maybe could do that, because I needed it.
DOERING: Well, we're definitely living in a time when I mean, certainly yearning for a cafe for being able to sit there and watch the people going by feels like a different world. It's such a strange time that we're living in where, you know, people are flocking so much to parks--or were--that cities had to shut them down. I mean, the Luxembourg Gardens has been temporarily closed, I was reading.
FREEMAN: Yeah.

Parisians and visitors enjoying an autumn afternoon in the Luxembourg Gardens. (Photo: Jeanne Menjoulet, Flickr CC BY-ND 2.0)
DOERING: I think because of that concern about spreading the virus. What do you think that our current hunger for park spaces can tell us about these places and what they like really mean to us?
FREEMAN: Well, given all the restrictions we've spoken about so far about who's letting in a park and what hours, they still are a powerful democratizing influence in cities, and I think in the last 10 to 15 years--I'm gonna sound like a Luddite--but we've been sold through the internet, this idea of public space online, which tends to, I think, in many ways destroy actual physical public space, because it draws people into these imaginary spaces, these digital spaces, whereas the public ones are not used as much as they used to be. But I hope this pause as horrible as it's going to be, if we can get through it, if we can survive, it makes us remember that public space can be a really beautiful, enlarging thing, especially parks, that they're there for us to be in to share with other people that there's nothing so beautiful as sitting on a park bench and having a picnic. You know, whatever you're eating, you know, it's ennobled by a tree looking down on you and if we get out of this I think there's gonna be a flood of people going to parks. Sometimes if I feel really low, I imagine that, imagine the kinds of, you know, coming out parties that we're going to have when August is over. But in the meantime, I think we have to go there in our mind. All of us hopefully have a, have a memory or two being taken to a park.

Bronze sculpture of Narcissus in the Jardin du Luxembourg. (Aparajith Bharathiyan, Flickr CC BY-NC-ND 2.0)
DOERING: So it's hard to pick a favorite but the poem from your book that I keep coming back to you, especially right now is called 'The Folded Wing'. Could you please read that poem for us?
FREEMAN: Do you ever see something and just looking at it, you realize a whole scale of kind of capacities for self care kind of exist within us, and that if you've been listening to only a certain part of your body, and I, I was in the park one day, and I saw this bird just kind of floating in circles, and it had tucked its beak into its wing, and I thought, yeah, yeah, feels kind of good to cuddle yourself. And it was one of those days where I just, I'd had a long day and I was feeling pretty, pretty grimy and the news was terrible. Everything was upsetting. And I looked at this bird and I thought, yeah, so I wrote this poem called 'The Folded Wing'.
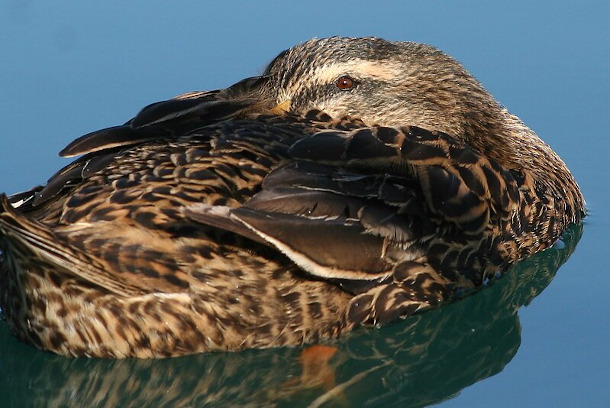

A lone mallard drifts and slips her beak beneath her wing. (Photo: Brent Myers, Flickr CC BY 2.0)
The lone duck in
Medici Fountain
slips her beak
beneath a wing
and falls asleep.
Drifting like a
hat tossed into
a green pond.
How good it feels
to be one's own
comfort, to discover
all the warmth we
need buried in
our bodies. Yes
we bleed, we are
broken, we get
just one body, yet,
there it lies most of
the time, calling
to us, saying, rest here,
lie down in me, I
am more than less
than you, even in a
world that treats
us as two.
DOERING: It's so lovely. It's, I found it so comforting.
FREEMAN: Oh, thanks.

John Freeman is an American writer and literary critic. (Photo: Deborah Treisman)
DOERING: Yeah, especially you know this, how good it feels to be one's own comfort like you said, you know, we can cuddle ourselves, we can find comfort in just being in our bodies.
FREEMAN: That's why I think parks are so soothing. There is something enormously comforting about being in a world where nature abounds. And when you can find a space, a public space, which even if it's built, even if it's crafted, even if it's kind of a fiction, you're around trees and ducks and birds and animals and light and air and shade and insects and water, and you feel this sort of age-old force, calling to you
CURWOOD: That's author, critic and editor John Freeman, speaking with Living on Earth's Jenni Doering about his new book of poetry, "The Park".
Related links:
- About The Park by John Freeman
- Learn more about the Jardin du Luxembourg in Paris, France
[MUSIC: Eric Tingstad, “Trails End” on Southwest, by Eric Tingstad, Cheshire Records]
CURWOOD: Living on Earth is produced by the World Media Foundation. Our crew includes Naomi Arenberg, Bobby Bascomb, Paloma Beltran, Thurston Briscoe, Jenni Doering, Anne Flaherty, Jay Feinstein, Don Lyman, Isaac Merson, Aynsley O’Neill, Jake Rego, and Jolanda Omari. And we welcome Kori Suzuki this week. Tom Tiger engineered our show. Alison Lirish Dean composed our themes. You can hear us anytime at L-O-E dot org, Apple Podcasts and Google Podcasts, and like us, please, on our Facebook page - Living on Earth. We tweet from @livingonearth. And find us on Instagram at livingonearthradio. I’m Steve Curwood. Thanks for listening!
ANNOUNCER: Funding for Living on Earth comes from you, our listeners, and from the University of Massachusetts, Boston, in association with its School for the Environment, developing the next generation of environmental leaders. And from the Grantham Foundation for the protection of the environment, supporting strategic communications and collaboration in solving the world’s most pressing environmental problems. Support also comes from the Energy Foundation, serving the public interest by helping to build a strong, clean, energy economy.
ANNOUNCER 2: PRX.
Living on Earth wants to hear from you!
Living on Earth
62 Calef Highway, Suite 212
Lee, NH 03861
Telephone: 617-287-4121
E-mail: comments@loe.org
Newsletter [Click here]
Donate to Living on Earth!
Living on Earth is an independent media program and relies entirely on contributions from listeners and institutions supporting public service. Please donate now to preserve an independent environmental voice.
NewsletterLiving on Earth offers a weekly delivery of the show's rundown to your mailbox. Sign up for our newsletter today!
 Sailors For The Sea: Be the change you want to sea.
Sailors For The Sea: Be the change you want to sea.
 The Grantham Foundation for the Protection of the Environment: Committed to protecting and improving the health of the global environment.
The Grantham Foundation for the Protection of the Environment: Committed to protecting and improving the health of the global environment.
 Contribute to Living on Earth and receive, as our gift to you, an archival print of one of Mark Seth Lender's extraordinary wildlife photographs. Follow the link to see Mark's current collection of photographs.
Contribute to Living on Earth and receive, as our gift to you, an archival print of one of Mark Seth Lender's extraordinary wildlife photographs. Follow the link to see Mark's current collection of photographs.
 Buy a signed copy of Mark Seth Lender's book Smeagull the Seagull & support Living on Earth
Buy a signed copy of Mark Seth Lender's book Smeagull the Seagull & support Living on Earth