Plastic Bag Bans and Pushback
Air Date: Week of March 8, 2024
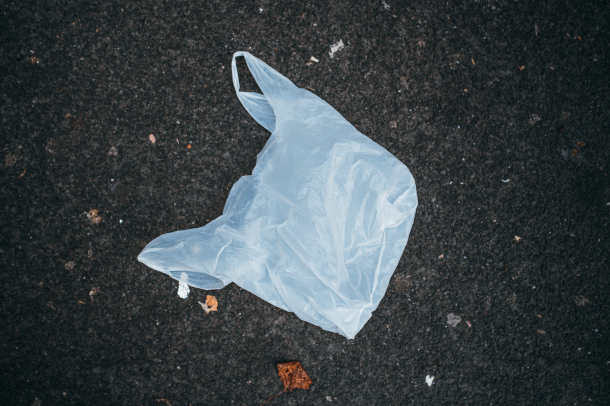

A “loophole” in a 2014 California law banning single-use plastic bags at checkout allowed slightly thicker plastic bags to be used instead, leading to more plastic bag pollution by weight. California lawmakers have now introduced a new bill to ban all plastic bags at checkout. (Photo: Ivan Radic, Flickr, CC BY 2.0)
A decade ago California became the first US state to ban single-use plastic bags, and eleven states followed suit. But some 18 other states have gone in the opposite direction and even blocked local cities and towns from prohibiting single use plastic bags. Judith Enck, President of Beyond Plastics and a former EPA Regional Administrator, joins Host Paloma Beltran to discuss successes and setbacks for efforts to minimize plastic bag waste.
Transcript
CURWOOD: It’s Living on Earth, I’m Steve Curwood.
BELTRAN: And I’m Paloma Beltran.
A decade ago, California became the first US state to ban single-use plastic bags, and 11 states as well as some territories followed suit. But some 18 other states have gone in the opposite direction and even blocked local cities and towns from prohibiting single-use plastic bags. And now Florida appears ready to join them, with a proposed statewide measure to bar local cities and towns from banning single-use plastic items. Against that trend there is now a proposal in California to update its pioneering law and eliminate loopholes that have apparently led to more plastic waste, not less. Here to discuss is Judith Enck, former EPA Regional Administrator and President of Beyond Plastics. Welcome back to Living on Earth, Judith!
ENCK: I always love being on Living on Earth. Thank you.
BELTRAN: We always love to have you. So I understand that legislators in California are now trying to correct or fix legislation from 2014 that banned single-use plastic bags in the state. What was the substance of that original legislation and in what ways did it not turn out as planned?
ENCK: Well, the public is really tired of seeing plastic bags everywhere in our communities. You look up in trees, you see plastic bags, you see it littered at beaches and parks. And so the state of California actually went first and passed a statewide ban to prohibit supermarkets and retail stores from handing out single-use plastic bags. Because they went first, they didn't have the benefit of knowing about mistakes in drafting the law. And unfortunately, they made a mistake, and they only banned thin film bags. And then the response from supermarkets and plastic bag makers were to then sell thicker single-use plastic bags, and kind of mislead the public and try to get people to think that these were actually reusable bags when most of them really weren't. So in fact, it made the status quo worse. We went from millions of thin plastic bags to millions of thick plastic bags that were typically only used once or twice. Thankfully, California lawmakers recognized that the original plastic bag ban is not working well at all. And so they've introduced a bill to fix it and not have it just say that they're banning thin film plastic bags, but all plastic bags, and that's the common-sense way to approach it. That's what the state of New York and other states have done.
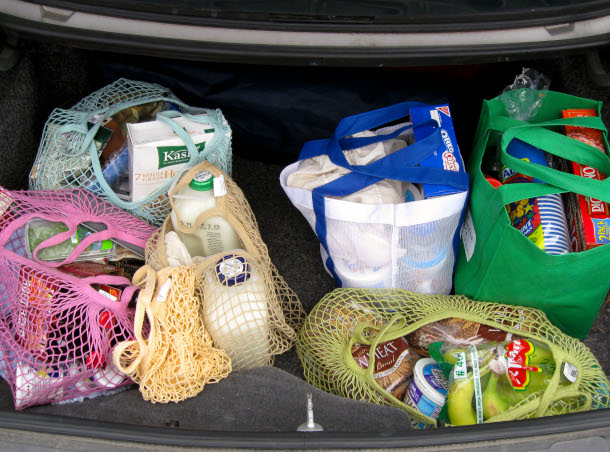

New Jersey's single-use plastics reduction law, NJ SB 864 / AB 1978 bans both plastic and paper bags at supermarket checkouts. Some consumers opt for bringing their own reusable bags like the ones pictured above. (Photo: Tim Samoff, Flickr, CC BY-ND 2.0)
BELTRAN: So you mentioned New York—what are some of the states that have made progress on plastic bag pollution, and that California might look up to as a model?
ENCK: I would look to New York and New Jersey as good models to reduce plastic bag pollution. The New York law bans all plastic bags at retail checkouts, full stop. You're not supposed to be receiving any kind of plastic bag whatsoever. And in New Jersey, we have that same law. But New Jersey went a step even further to promote reusable bags by also banning paper bags at the checkout, which was a surprise. And that initiative actually came from the supermarket companies. They opposed the original plastic bag ban. But once they saw that New Jersey lawmakers were going to pass it into law, they were worried that many consumers might not bring reusable bags and would ask for paper bags, which are more expensive than plastic bags. So in a twist, the supermarket lobby said, don't just ban plastic bags—if you're going to do that, ban paper bags as well. And that is the law in New Jersey. And so you've seen a very significant shift toward consumers consistently bringing their own reusable bags to the store.
BELTRAN: So what has been the plastic industry's response to these plastic bag bans?
A tracking study by ABC News found that plastic bags dropped off for recycling often end up in landfills or incinerators. (Photo: A.Davey, Flickr, CC BY-NC-ND 2.0)
ENCK: Oh, the plastic industry always opposes these plastic bag bans, or they try to make them weaker. The other thing they've done in some states is adopt state laws prohibiting local governments from banning plastic bags. It's always interesting to watch the trajectory toward when you get a statewide plastic bag ban. It often happens first at the city or municipal level, and then it trickles up to the state level. And whether it's your city council, or your state legislature, if they have proposed anything to reduce plastic bag pollution, the plastics industry shows up in force fighting these proposals. The excuse they use on why we shouldn't ban plastic bags is they say we can just recycle plastic bags. But plastic bag recycling has been an abysmal failure. There have been some journalism projects whereby little electronic trackers were put inside plastic bags that you drop off in your supermarket recycling bin, and oftentimes the plastic bags are tracked to landfills or incinerators. So I'm really losing confidence in any ability to even recycle single-use plastic bags. Once states adopt these laws, using reusable bags just becomes second nature. So it's just a matter of passing a good law, no loopholes like the California law, strict enforcement. And we save literally hundreds of millions of plastic bags in states every single year.
BELTRAN: Yeah. And speaking about local decision making on plastic issues, in Florida, the state legislature is working on a law known as "ban on bans" that will impact local decision making on plastic issues. Can you tell me more about that?

Judith Enck is president of Beyond Plastics and former Regional Administrator for Region 2 of the EPA. (Photo: Courtesy of Judith Enck)
ENCK: Yes. This is a very sinister move by the plastics industry. They know that the public is tired of seeing plastic litter all over communities, entering rivers and the ocean, affecting our own health. And so there's a real interesting and strong grassroots movement to reduce plastics, for many reasons—climate change reasons, environmental justice reasons, health reasons, and a realization that plastic recycling mostly doesn't work. So at the local level, many volunteers come together, they petition their city council or their county government. And they want to adapt a local plastic bag ban, or perhaps a ban on polystyrene foam food containers. Another popular move is something called "skip the stuff." So when you order takeout food, you don't automatically get all the plastic utensils and condiments and straws. So we're seeing this growing movement against plastic pollution all over the country. So the reaction by some state legislators—at the request of the plastics, chemical and fossil fuel lobbyists—is to adopt what's called a ban on bans. So in Florida, they are considering adopting a law that says local communities cannot adopt local laws dealing with plastics. These bans on bans have been adopted in at least 18 states, including states like Texas and Oklahoma. And they sure seem to be anti-democratic. You have the state government telling local government they cannot act to protect the environment and health in their communities. It's a shrewd move. And it's really unfortunate that state lawmakers and governors are blocking progress at the local level to reduce plastic pollution.
BELTRAN: Judith Enck is a former EPA Regional Administrator and president of Beyond Plastics. Thank you so much for joining us.
ENCK: My pleasure. Thank you.
Links
Check out the list of local bag bans in California
Los Angeles Times | “California’s Plastic Bag Ban Is Failing. Here’s Why”
Learn more about Beyond Plastics
ABC News | “We Put Dozens of Trackers in Plastic Bags for Recycling. Many Were Trashed.”
Read about New Jersey’s Legislation Banning Single-Use Paper and Plastic Bags
Living on Earth wants to hear from you!
Living on Earth
62 Calef Highway, Suite 212
Lee, NH 03861
Telephone: 617-287-4121
E-mail: comments@loe.org
Newsletter [Click here]
Donate to Living on Earth!
Living on Earth is an independent media program and relies entirely on contributions from listeners and institutions supporting public service. Please donate now to preserve an independent environmental voice.
NewsletterLiving on Earth offers a weekly delivery of the show's rundown to your mailbox. Sign up for our newsletter today!
 Sailors For The Sea: Be the change you want to sea.
Sailors For The Sea: Be the change you want to sea.
 The Grantham Foundation for the Protection of the Environment: Committed to protecting and improving the health of the global environment.
The Grantham Foundation for the Protection of the Environment: Committed to protecting and improving the health of the global environment.
 Contribute to Living on Earth and receive, as our gift to you, an archival print of one of Mark Seth Lender's extraordinary wildlife photographs. Follow the link to see Mark's current collection of photographs.
Contribute to Living on Earth and receive, as our gift to you, an archival print of one of Mark Seth Lender's extraordinary wildlife photographs. Follow the link to see Mark's current collection of photographs.
 Buy a signed copy of Mark Seth Lender's book Smeagull the Seagull & support Living on Earth
Buy a signed copy of Mark Seth Lender's book Smeagull the Seagull & support Living on Earth