Facing the Biodiversity Crisis
Air Date: Week of November 1, 2024

Palawan Island is the largest in the Philippines and is known as “The Last Ecological Frontier of the Philippines." (Photo: Patrick Kranzmüller, Flickr, CC_BY_NC_ND_2.0)
As the world meets in Cali, Colombia at the 2024 UN biodiversity summit, we speak with KM Reyes, co-founder of the Centre for Sustainability Philippines, in a conversation first broadcast in 2022 about how indigenous people are often vital protectors of land and biodiversity. She joined Host Steve Curwood to describe indigenous land protection on the island of Palawan in the Philippines.
Transcript
DOERING: It’s Living on Earth, I’m Jenni Doering.
CURWOOD: And I’m Steve Curwood.
According to the United Nations, some 1 million species are at risk of going extinct within decades. To try to avert that grim future, the world’s nations are meeting in Cali, Colombia, at the 2024 UN biodiversity summit known as COP16. The last round of talks in 2022 yielded an agreement to protect 30% of the earth’s lands and oceans by 2030, simply known as “30 by 30.” But protecting those vast areas isn’t as simple as putting up a “keep out” sign, because humans, especially indigenous peoples, are often vital protectors of land. In 2022 Filipino conservationist KM Reyes joined us to discuss how indigenous practices can safeguard biodiversity. Here’s an excerpt from our conversation.
REYES: Yeah, so the Philippines is one of only 17 mega-biodiverse countries on the planet. It was previously 95% covered in pristine rainforest, and now only 3% is left.
CURWOOD: Whoa, wait, you've lost all but the last 3%?
REYES: Yes, of pristine rainforest.
CURWOOD: Wow. Okay.
REYES: And even though we only have 3% of pristine rainforest left, we actually still have the most vertebrate diversity on the planet. So, we're a really small country, we're made up of 7,000 islands. But we still have incredible biodiversity across our islands, and also in our oceans, so our coral reefs and our seas. We have all sorts of really charismatic wildlife and ocean fauna, from thresher sharks to the Philippine pangolin, which is critically endangered and the number one poached animal globally. And this area is also this perfect meeting place of volcanoes and the Coral Triangle. So, it's a meeting place for all sorts of different, you know, tectonic movements that happened. And that's why we are also really mega biodiverse. And the reason why this specific treaty is so important for us in the Philippines is if we don't have a good global strategy, then we don't have a national strategy to build off. And obviously, as a conservationist, I want the strongest possible policies at the international level, as well as at the national level. And if we're going to reach our biodiversity targets, if we're going to reach these very ambitious goals, we need adequate financing to do it, especially with something like 30 by 30, that requires a lot of follow up monitoring and management of these protected areas.
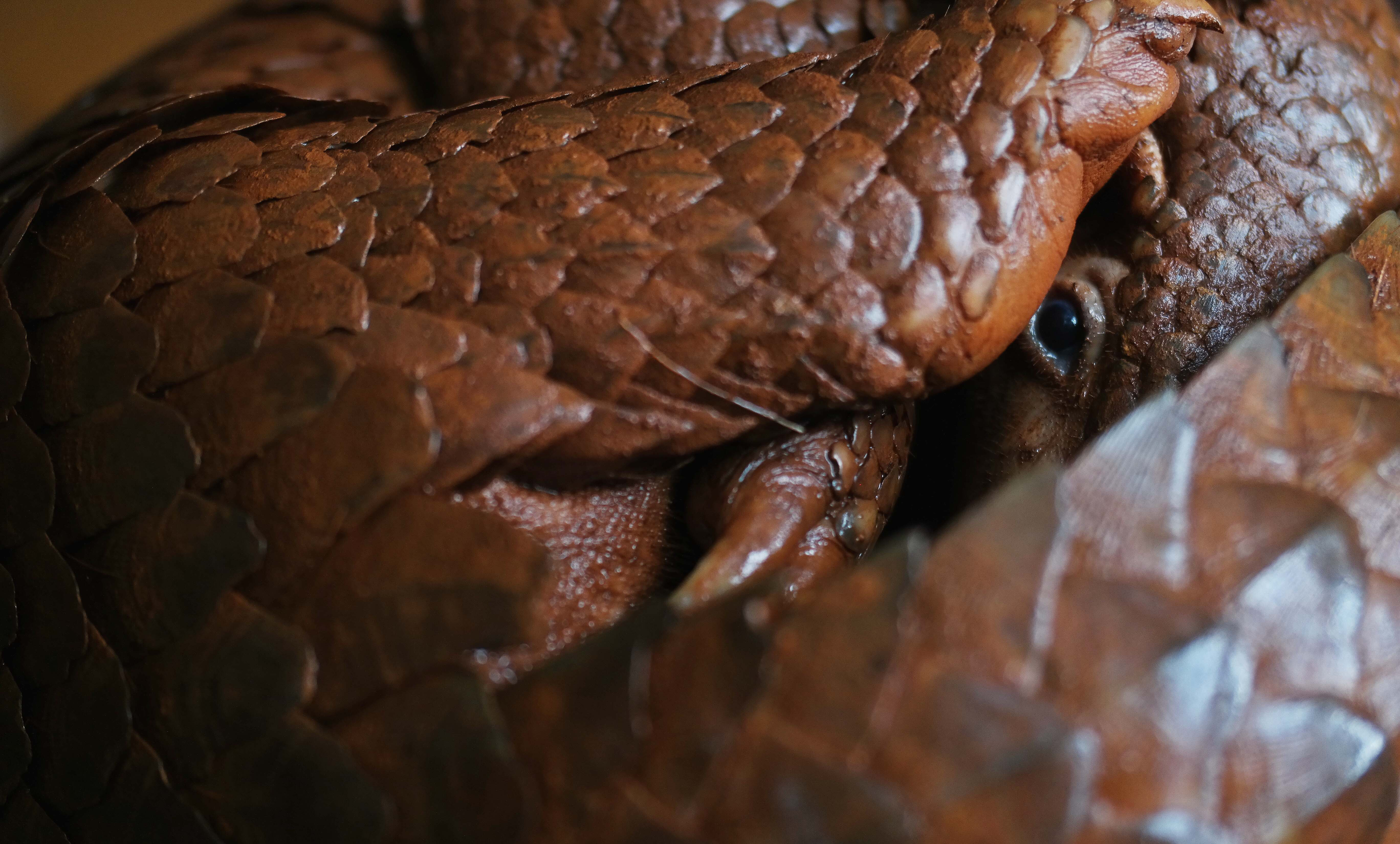

Palawan Pangolin. Pangolins are among the most critically endangered animals due to heavy poaching and worldwide trafficking. (Photo: John Christian Yayen)
CURWOOD: Tell me a bit more about the role of the Global North here and why financing is necessary to help protect the biological diversity in the Philippines.
REYES: Yeah, so a lot of the environmental destruction is often caused by Global North and industries in the Global North. And so, there is a lot of importance here on ensuring that the Global North also pays their dues. For example, you know, we're working on a protected area in Palawan. And we're up against a mining company that is Canadian, funnily enough. And so, these are the kinds of international and kind of transnational issues that we deal with when trying to protect biodiversity. And so, it's extremely important that the Global North really takes responsibility for the footprint that they're making on biodiversity in different areas, especially in the Global South. And you will see this across mega-biodiverse, you know, Global South countries, the Democratic Republic of Congo is another classic example, whether it's cobalt or nickel, or, you know, other kinds of minerals. And specifically in the Philippines, the big issue that we're dealing with is that we're very rich in nickel. And so, this is obviously a key mineral for the electric car revolution. And so, for us, in the Philippines, it's very far away in our timeline that we're going to have access to these electric cars, right? A lot of these electric cars will go to Europe and North America, but they're coming from and destroying biodiversity in Global South countries like the Philippines.

Indigenous Batak mothers of Manggapin. (Photo: Jessa Garibay)
CURWOOD: Now, what about the Indigenous communities living within the islands there, what's their role in protecting biological diversity?
REYES: So Indigenous peoples globally represent 5% of total population and protect 80% of global biodiversity. So Indigenous peoples and local communities play an outsized role in ensuring that biodiversity continues. And actually, the reason why we still have biodiversity now is because of our Indigenous peoples and local communities that are living in and around our frontlines and protecting these areas, whether it's freshwater and salmon runs to pristine rainforest. Certainly, in the area that we protected, at Cleopatra's Needle Critical Habitat, this is home to the disappearing Batak tribe, there's only 200 people left of this ethnic group, and they have protected this area since time immemorial. So, wherever we are in the world, Indigenous peoples and local communities are the key to ensuring that these areas are protected, and biodiversity is retained.

Batak women and children in traditional dress. (Photo: Jessa Garibay-Yayen)
CURWOOD: Yeah, tell me more about Cleopatra's Needle. Your organization, the Center for Sustainability PH worked on helping to protect this area. Why is it so important?
REYES: Cleopatra's Needle Critical Habitat is the Philippines' biggest critical habitat. It's the size of the City of Montreal, so some 41,350 hectares, and it's the highest peak of our city, Puerto Princesa city. It's about 1500 meters above sea level, it takes about four days to hike up to the peak because it's extremely difficult terrain to get up. And it's pristine rainforest, as I mentioned, that is the ancestral home of the Indigenous Batak tribe. And with summary scientific research, we've already been able to identify that it's home to 61 Palawan endemic species and 31 globally threatened IUCN species. So, it's an area of extremely important biological diversity. And it's also very important as a critical habitat, because this is habitat that's critical for the survival of a very, very special and threatened species globally, not just in the Philippines. So, this area is magical. It's, you know, flowing rivers and pristine rainforest, the hiking is incredible. It's an area that has many, many sacred spots, and is tied with the culture and tradition of the Indigenous Batak community. And I think without their stewardship, we would not have Cleopatra's Needle, for sure. And also, without this forest remaining, the Batak people would also not survive, they are so tied with this forest that for them, their existence could not be without it. And so, for example, you know, their naming of how they name their children is always about, what are the natural things that are around them at the time of birth. So sometimes they're named after the tree that they're born under, or the weather on the day of their birth. It's very much tied in with specifically this rainforest.
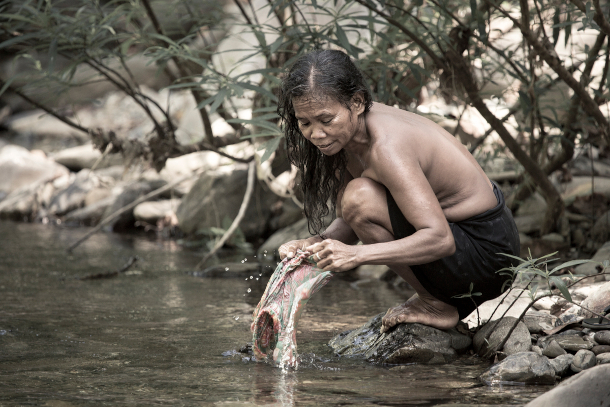

A Batak woman washing clothes in the river. (Photo: Robin Moore)
CURWOOD: By the way, why is it called Cleopatra's Needle? That doesn't sound like an Indigenous term to me anyway!
REYES: Yeah, so Cleopatra's Needle is a military name that came from the US, because it was the US military that mapped most of our island, but it does actually have an Indigenous name. So, Cleopatra's Needle is named after the obelisk peak of the mountain, but Puyos ni Bayi is the Indigenous name. And this means the hair bun of Bayi. So Bayi is a common foremother of the Indigenous Batak people, so generations before she was seen as the foremother of their people. And puyos means hair bun. So, they see it as the hair bun at the top. And that's what makes it so pointy. And so, they see Bayi as the protector of this forest. So internally, we talk about it as Puyos ni Bayi, but internationally, it's called Cleopatra's Needle.

A Batak woman and children fish in the river. (Photo: Robin Moore)
CURWOOD: KM Reyes is Co-Founder of the Centre for Sustainability Philippines. Since we spoke with her in 2022 there have been legal challenges to mining on the island of Palawan, and in 2023 the Philippine Supreme Court ordered a nickel mining venture there to take proper care of the environment and people. The UN biodiversity conference COP16 is scheduled to wrap up on Nov. 1 and during next week’s broadcast we plan to dive into what took place, so don’t forget to tune in!
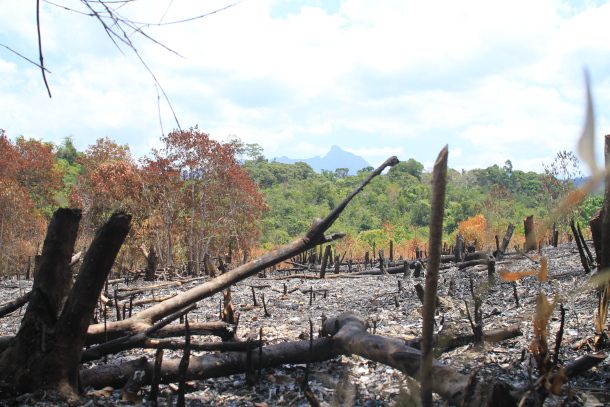

Burned rainforest near Cleopatra’s Needle in the Philippines. (Photo: Jessa Garibay-Yayen)
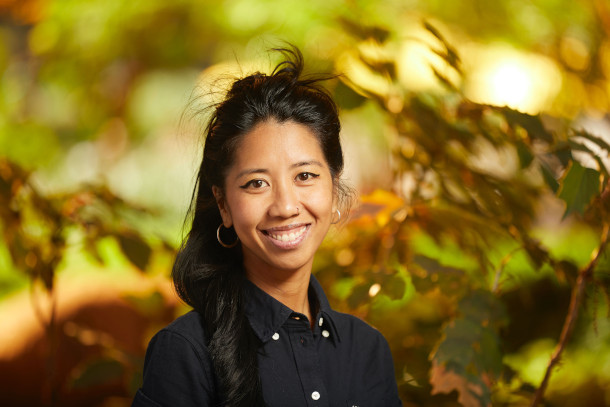

KM Reyes is a conservation lobbyist, community organizer, and National Geographic Explorer, based on Palawan Island, the Philippines. She’s the Co-Founder & Advisor of the environmental non-government organization, Centre for Sustainability PH, which she co-founded together with a small group of local colleagues. Their mission is to conserve the Philippines’ last remaining 3% of pristine rainforest through the legal establishment of protected areas. (Photo: Courtesy of KM Reyes)
Links
Centre for Sustainability PH Instagram
Learn more about Centre for Sustainability
Living on Earth wants to hear from you!
Living on Earth
62 Calef Highway, Suite 212
Lee, NH 03861
Telephone: 617-287-4121
E-mail: comments@loe.org
Newsletter [Click here]
Donate to Living on Earth!
Living on Earth is an independent media program and relies entirely on contributions from listeners and institutions supporting public service. Please donate now to preserve an independent environmental voice.
NewsletterLiving on Earth offers a weekly delivery of the show's rundown to your mailbox. Sign up for our newsletter today!
 Sailors For The Sea: Be the change you want to sea.
Sailors For The Sea: Be the change you want to sea.
 The Grantham Foundation for the Protection of the Environment: Committed to protecting and improving the health of the global environment.
The Grantham Foundation for the Protection of the Environment: Committed to protecting and improving the health of the global environment.
 Contribute to Living on Earth and receive, as our gift to you, an archival print of one of Mark Seth Lender's extraordinary wildlife photographs. Follow the link to see Mark's current collection of photographs.
Contribute to Living on Earth and receive, as our gift to you, an archival print of one of Mark Seth Lender's extraordinary wildlife photographs. Follow the link to see Mark's current collection of photographs.
 Buy a signed copy of Mark Seth Lender's book Smeagull the Seagull & support Living on Earth
Buy a signed copy of Mark Seth Lender's book Smeagull the Seagull & support Living on Earth